Automate End-to-End Testing: Manual Triggering with GitHub Actions and Browser Selection
Unlock the power of GitHub Actions for more controlled End-to-End testing. Learn how to trigger tests manually with parameters and select your desired browser directly from the UI.
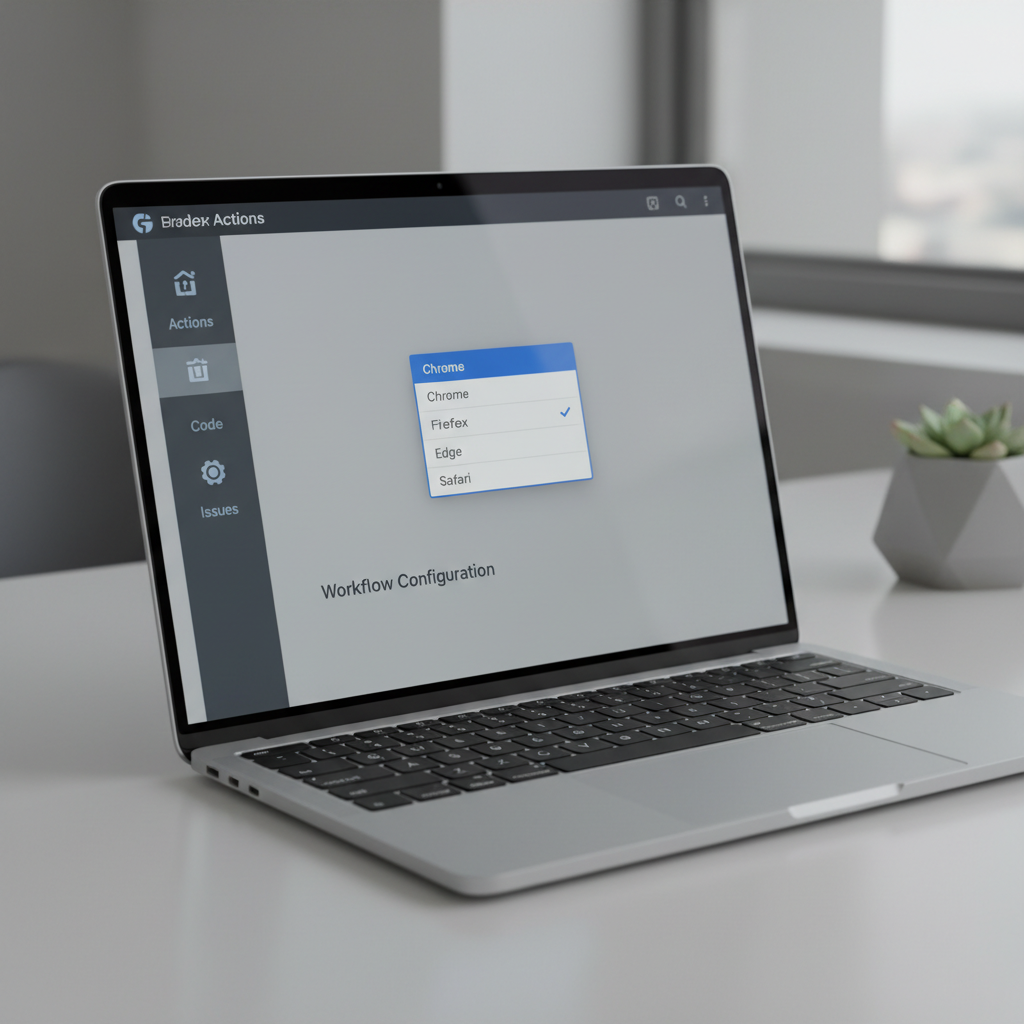
Streamlining End-to-End Testing with GitHub Actions: Manual Triggers and Browser Selection
In the fast-paced world of software development, robust End-to-End (E2E) testing is crucial for ensuring application quality and reliability. GitHub Actions offers a powerful platform to automate your CI/CD pipelines, and with a few strategic configurations, you can significantly enhance your E2E testing process. This post explores how to leverage GitHub Actions for parameterized, manual E2E test triggering, complete with a user-friendly UI dropdown for browser selection, conditional dependency installation, and improved artifact uploads for better diagnostics.
The Challenge: Controlled and Flexible E2E Testing
Traditional automated E2E tests often run on every code commit, which can be resource-intensive and may not always align with specific testing needs. Sometimes, you need the flexibility to trigger tests manually, perhaps for a specific build, a particular environment, or to test a feature under specific conditions. Furthermore, efficiently testing across different browsers is essential for cross-browser compatibility, but managing this within automation can be cumbersome.
Solution: Parameterized Manual Triggers in GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions allows you to define workflows that can be triggered manually with inputs. This feature is invaluable for E2E testing scenarios where you require more control. By defining `inputs` in your workflow file, you can prompt users for specific values when they manually initiate a workflow run.
Implementing Manual Triggers
Consider a workflow that needs to run E2E tests. You can add inputs for the target environment, a specific test suite, and crucially, the browser to be used for testing.
Here’s a simplified example of how you might configure this in your workflow file:
name: Manual E2E Test Trigger
on:
workflow_dispatch:
inputs:
environment:
description: 'Target environment for E2E tests'
required: true
default: 'staging'
type: choice
options:
- development
- staging
- production
browser:
description: 'Browser to use for E2E tests'
required: true
default: 'chrome'
type: choice
options:
- chrome
- firefox
- edge
test_suite:
description: 'Specific test suite to run'
required: false
default: 'all'
When a user navigates to the Actions tab in their GitHub repository and selects this workflow, they will be presented with a form to input these values before triggering the run. This provides a clear, UI-driven way to customize test execution.
Enhancing Diagnostics: Conditional Dependency Installation
Different browsers or testing environments might require specific dependencies or configurations. Installing everything upfront can lead to longer build times and unnecessary resource consumption. GitHub Actions enables conditional logic within your jobs, allowing you to install dependencies only when needed.
Conditional Logic for Dependencies
For instance, if you are running tests on Firefox, you might need to install specific Gecko drivers. You can use the `if` condition in your workflow steps to manage this:
- name: Install Browser Dependencies
if: inputs.browser == 'firefox'
run: npm install --save-dev geckodriver
- name: Run E2E Tests
run: npm run test:e2e -- --browser=${{ inputs.browser }}
This approach ensures that your workflow is efficient, installing only what is necessary for the selected browser or environment, thereby reducing execution time and potential conflicts.
Improving Test Diagnostics with Artifact Uploads
When E2E tests fail, having detailed diagnostic information is critical for quick debugging. GitHub Actions allows you to upload files as artifacts, which are accessible after the workflow run completes. This is particularly useful for saving test reports, screenshots, or video recordings of test failures.
Configuring Artifact Uploads
You can configure your testing framework to generate detailed logs or screenshots upon failure and then use the `actions/upload-artifact` action to store them.
- name: Upload Test Artifacts
if: failure() # Upload only if the previous step failed
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
with:
name: test-logs-${{ github.run_id }}
path: ./test-results/
This ensures that even if a test fails, you have immediate access to the necessary data to diagnose the issue, significantly speeding up the debugging process.
Pros and Cons of Parameterized Manual E2E Testing
Pros:
- Enhanced Control: Manually trigger tests with specific parameters for targeted testing.
- Improved Efficiency: Run tests only when needed, saving CI/CD resources.
- Cross-Browser Testing Simplified: Easily select desired browsers via a UI dropdown.
- Better Diagnostics: Conditional dependency installation and comprehensive artifact uploads aid debugging.
- Reduced Execution Time: Install only necessary dependencies, speeding up test runs.
Cons:
- Manual Overhead: Requires human intervention to trigger, unlike fully automated runs.
- Potential for Misconfiguration: Users might select incorrect parameters if not careful.
- Complexity: Setting up parameterized workflows requires a deeper understanding of GitHub Actions syntax.
Driving Adoption and Further Learning
Implementing these strategies in your projects can significantly improve the efficiency, control, and diagnostic capabilities of your E2E testing. By embracing parameterized manual triggers and UI-driven browser selection, development and QA teams can ensure higher quality software with less friction.
For a more in-depth understanding and advanced configurations, I highly recommend exploring the official GitHub Actions documentation. It provides comprehensive guides and examples that can help you tailor these techniques to your specific needs.
Explore further: GitHub Actions Documentation on Manual Triggers
By integrating these practices, you empower your team to perform more targeted, efficient, and insightful End-to-End testing, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable software releases.